Mid-frequency direct current (MFDC) welding and alternating current (AC) welding are two commonly used welding processes, each with its own characteristics. In this article, we’ll analyze together which one has the upper hand: MFDC welding or AC welding?
Working Principles:
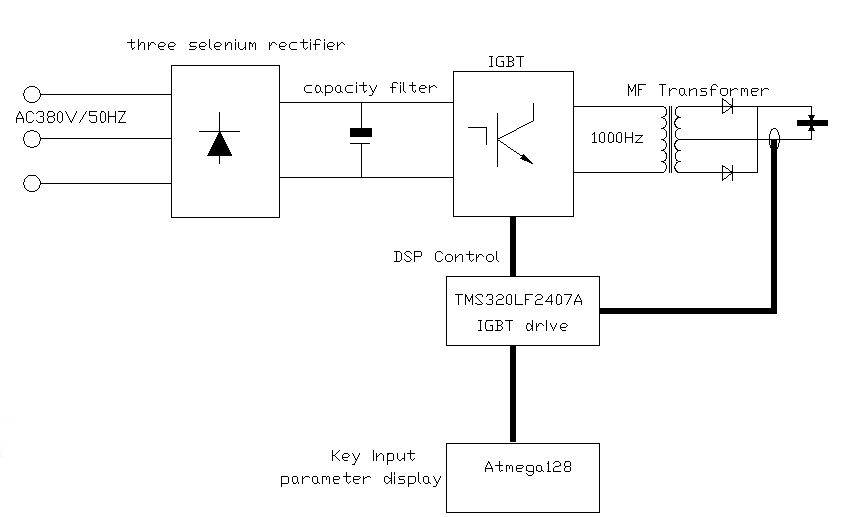
MFDC/Inverter Welding Machine:
Firstly, three-phase AC voltage passes through rectifiers for filtering.
Secondly, IGBT switches convert the current into a mid-frequency current of 1000 Hz and transmit it to the welding transformer.
Finally, high-power rectifier diodes output the welding current as stable direct current (DC).
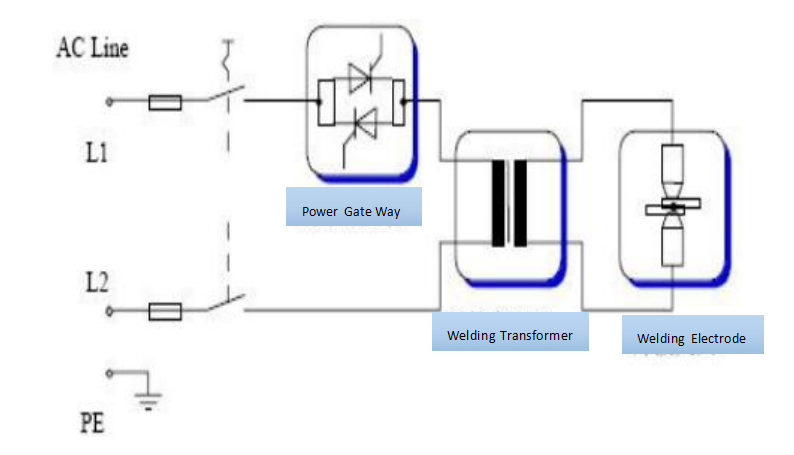
AC Welding Machine:
The power input is AC, which, after passing through the power switch, enters the main circuit and control circuit.
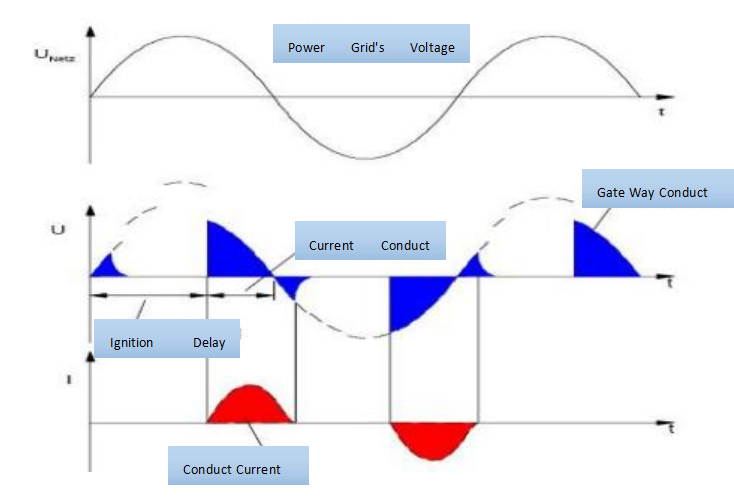
The transformer steps down the high-voltage AC to a low-voltage AC suitable for welding. AC current alternates between positive and negative, generating heat as it passes through the welding rod and workpiece, thereby melting the welding material and achieving welding.
Advantages of MFDC Welding over AC Welding:
High Stability:
MFDC welding is recognized internationally as one of the high-end resistance welding products, enhancing stability during welding. Its friendly welding process parameters and wide adaptability range of secondary current truly maintain constant current, offering broader prospects than AC welding.
The MFDC power source outputs minimal waveform, avoiding current peak impacts and minimizing splashing during welding.
Adjustment of MFDC welding current occurs at a rate of 1000 times per second, achieving millisecond-level precision, which is over 20 times more accurate than traditional AC welding machines.
MFDC welding is not affected by the shape and material of the workpiece, eliminating inductive losses.
High Efficiency:
MFDC welding machines achieve a welding power factor of over 98%, while AC machines are around 60%, indicating significantly improved efficiency in MFDC welding.
Low Operating Costs:
Due to the substantially increased initial value of welding current, actual welding time is shortened by over 20%, greatly reducing the demand for welding pressure.
The requirements for factory power supply are lower, only about 2/3 of AC welding machines, and even with fluctuations in power supply voltage, MFDC welding machines can still precisely control welding current.
Therefore, power consumption of MFDC welding machines is significantly reduced, achieving energy savings of over 40%. Additionally, using three sets of balanced loads ensures that no group is overloaded, meeting the requirements for economic energy conservation.
Lightweight:
Compared to AC welding machines, the welding transformer of MFDC machines is significantly lighter, making the equipment more portable and convenient. It weighs only one-third of the AC transformer’s weight and volume, suitable for robot welding systems.
Environmentally Friendly:
Eliminating pollution to the power supply, MFDC welding is a green welding method that does not require a separate power supply and can be used together with robot welding fixture control systems.
In summary, MFDC welding surpasses AC welding in terms of welding stability, quality, efficiency, energy saving, lightweight equipment, and reduced power requirements for the power supply system.
Agera offers a full range of mid-frequency spot welding machines, with MFDC resistance welding technology reaching an international advanced level. The maximum short-circuit current reaches 250,000 amperes, widely used in various alloy steels, high-strength steels, hot-formed steels, and aluminum alloy spot welding processes, providing high-end equipment and reliable services to many world-renowned Fortune 500 companies.
Post time: Mar-26-2024